Innovative Client Technologies Blog
Your Password Can Probably be Cracked Faster Than You’d Think
Whether you’re talking about identity theft, data breaches, or any other form of cybercrime, one of the leading causes of successful cyberattacks is the use of insufficiently secure passwords. Just how easy is it for someone to bypass such a password? Let’s consider the facts.
How to Crack a Password
Cybercriminals come correct, first of all. Not only do many of them have access to some pretty sophisticated tools and resources, they go about their selfish and deceitful activities with a strategy based on the average user’s online conduct.
For the cybercriminal, bypassing a password is really a numbers game. Chances are good that, if they try some commonly used passwords, a cybercriminal will eventually hit pay dirt. For instance, a cybercriminal’s first guesses could look like the following:
- 123456789
- guest
- qwerty
- password
- a1b2c3
Since these are some of the world’s most common passwords—with an estimated 10 to 20% of accounts using a similar password—trying different variations of them or adding one or two symbols gives a cybercriminal a pretty good chance of getting in.
If we imagine ourselves to be cybercriminals, this knowledge helps to simplify our process immensely. If we invest in a password cracking tool, which effectively just tries every dictionary word and randomized combination of characters, increasing in length as it goes, chances are good that we will ultimately get in.
It’s just like trying to guess a combination lock number. While it’s going to take some time, you could try every possible combination—1-1-1, 1-1-2, 1-1-3—until you either get it, or the bike’s owner is back and not-so-politely asking you to step away from their property.
The more variables there are to try, the more possible options there are—increasing at exponential rates, making it impossible to manually try every single combination. A computer, on the other hand, could try…and much, much faster. That’s how a password-cracking tool operates.
How Long Before a Password is Cracked?
It all depends on the password. Many of the tools that these cybercriminals will use will try the usual suspects first, and will therefore crack the password immediately. The shorter, weaker passwords can take fractions of a second, with these tools testing millions of potential credentials in that time.
It also depends on the hardware the cybercriminal is using, as a more powerful system will allow the attacker to test potential passwords that much faster. Let’s go over how speedily a reasonably powerful laptop could crack a password, based on how long the password is, and how complicated it is:
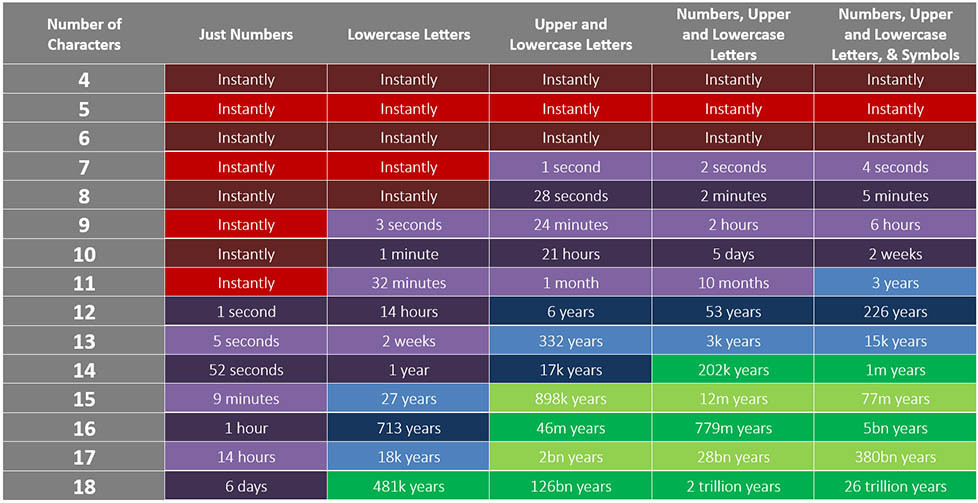
As pictured, weak—or short and simple passwords—would fold immediately, holding out for a few seconds or minutes at best. However, once a password is designed to be longer and more complex, the likelihood of a password being cracked within someone’s lifetime becomes far smaller…arguably impossible.
That is, however, assuming that your password’s length and complexity aren’t wholly reliant on a combination of otherwise common (and therefore, insecure) words or phrases. Sure, “!password12345” may seem to meet some of the basic requirements for a password—and based on the password chart above, should take a million years to figure out—the use of common password trends makes it far easier to figure out.
This is precisely why we always advocate for more stringent password practices to ensure each and every one is sufficiently secure. These practices include the aforementioned length and complexity requirements, and avoiding things that could be guessed somewhat easily, including pet names, birthdays, and other common factors. Of course, passwords should never be used more than once, as in, you need a separate password for each account you’re securing.
It is also important to keep in mind that the results generated above could be accomplished using resources that are out there and available, using a basic tool on a common laptop. An invested cybercriminal very well could have additional resources at their disposal, things like botnets and significant cloud resources, along with the hardware needed to power through a brute force attempt much faster than our hypothetical mid-range laptop could.
The big takeaway: ALWAYS use strong and secure passwords.
